Understanding Grain Storage: Why is Grain Stored in Silos?
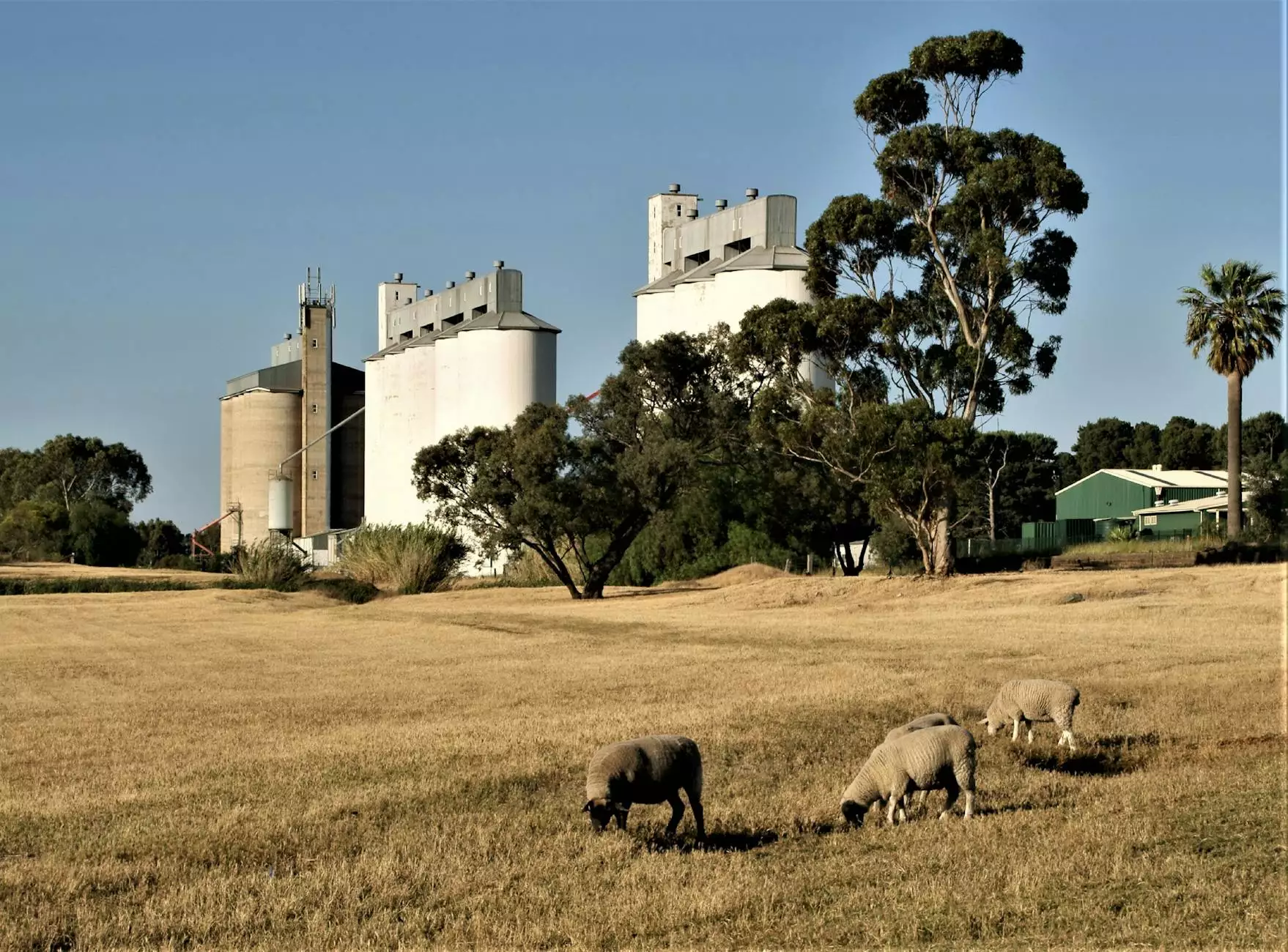

Grain storage is a crucial aspect of the agricultural industry, playing a vital role in maintaining the quality and availability of grains. One of the most effective and widely used methods for storing grain is through the use of silост. In this article, we will delve deep into the question: why is grain stored in silos? We will explore the various advantages of using silos, the types of grains typically stored, and how effective storage impacts the entire farming ecosystem.
The Role of Silos in Grain Storage
Silos are large, vertical structures designed to store bulk materials, particularly grain. Their primary purpose is to protect the grain from the elements and prevent spoilage from pests and rodents. Here are several key reasons why grain is stored in silos:
- Protection from Spoilage: Silos are airtight, which helps in protecting grain from moisture and air, both of which can lead to spoilage and mold buildup.
- Efficient Storage Space: Silos utilize vertical space effectively, allowing for large quantities of grain to be stored in a smaller footprint compared to traditional flat storage methods.
- Ease of Access: Silos are designed for easy loading and unloading of grain, facilitating better logistics and efficiency during harvest and distribution.
- Pest Control: The sealed environment of silos helps in minimizing pest infestations, which can be detrimental to grain quality and yield.
Types of Grains Stored in Silos
Different types of grains are stored in silos, each having specific storage requirements. Below are some common grains and their storage characteristics:
- Wheat: Wheat is often stored in silos due to its high demand and susceptibility to spoilage. Proper airflow and temperature control are vital during storage.
- Corn: Corn silos need to maintain the right moisture level to prevent fermentation and spoilage, making their design crucial.
- Barley: Barley is often stored in silos to protect it from pests and weather, ensuring quality for brewing and livestock feed.
- Rice: Silos for rice must be well-ventilated and protected from moisture to maintain its quality during long-term storage.
Why is Grain Stored in Silos? The Advantages Explained
Understanding why is grain stored in silos goes beyond merely recognizing their structural advantages. Here are detailed insights into the benefits that make silos indispensable for grain storage:
1. Enhanced Quality Preservation
One of the foremost reasons for storing grain in silos is the ability to preserve the quality of the grain over extended periods. Silos allow for:
- Controlled Atmosphere: By regulating temperature and humidity, silos provide an ideal environment that keeps grain dry and cool.
- Minimized Damage: Due to their robust construction, silos mitigate the risk of physical damage from weather and handling during transportation.
2. Improved Logistics and Workflow
Grain storage in silos also facilitates better operational workflow within farms and grain-handling operations. This efficiency encompasses:
- Streamlined Loading and Unloading: Modern silos are equipped with advanced technology that enhances the process of loading and unloading grain.
- Faster Turnaround Times: Quick access to stored grain allows farmers to respond promptly to market demands and avoid delays.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in silos can lead to long-term cost savings for farmers and agricultural businesses. This economic advantage arises from:
- Reduced Waste: By preventing spoilage, silos reduce the loss of grain, thus preserving the investment made in crops.
- Lower Storage Costs: Silos provide a more economical storage solution by allowing large quantities of grain to be stored securely.
Types of Silos and Their Uses
Understanding the types of silos can also shed light on why is grain stored in silos. Various silo designs cater to different storage needs:
1. Upright Silos
Upright silos are the most common design, typically made of steel, concrete, or fiberglass. They are favored for their:
- Space Efficiency: They maximize vertical space, making them suitable for smaller plots of land.
- Durability: Their robust construction can handle heavy loads and various weather conditions, ensuring longevity.
2. Bunker Silos
Bunker silos are horizontal and usually made of concrete bunkers. They are ideal for large-scale operations due to:
- Large Volume Storage: These are suitable for bulk storage of various types of feed and grains.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often less expensive to construct than upright silos.
3. Bag Silos
Bag silos utilize large, durable plastic bags for grain storage. They offer flexibility through:
- Mobility: Easier to set up and move, making them ideal for temporary operations or smaller farms.
- Affordability: Lower initial costs compared to traditional silos.
Impact of Silos on the Agriculture Industry
The significance of grain storage in silos extends beyond individual farm operations. It has a profound impact on the entire agricultural industry, including aspects like:
1. Supply Chain Efficiency
By providing secure and efficient grain storage, silos improve the overall supply chain. They enable farmers to:
- Smooth Demand Fluctuations: Stored grains can be released into the market during times of high demand, stabilizing prices.
- Ration Supplies: Silos allow for the careful management of grain supplies to avoid shortages.
2. Local and Global Trade
Grain silos play a pivotal role in facilitating local and international trade by:
- Maintaining Quality Standards: Quality grain storage in silos helps meet regulations and standards for exports.
- Streamlining Exports: Larger quantities of grain can be stored and prepared for shipment, enhancing trade opportunities.
Best Practices for Grain Storage in Silos
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on temperature and moisture levels to prevent spoilage.
- Proper Sealing: Ensure that all seals are intact to minimize air and moisture entry.
- Pest Management: Implement pest control strategies to safeguard the quality of stored grain.
- Periodic Cleaning: Regularly clean silos to prevent contamination and spoilage.
Conclusion
Understanding why is grain stored in silos gives us insight into the agricultural practices that help sustain food production and supply chains. Silos not only protect grain but improve economic efficiency, enhance logistics, and foster effective management of grain supplies. Whether you are a farmer, an agricultural business owner, or simply interested in farming technologies, the importance of silos in grain storage cannot be overstated.
At TSGC Inc., we recognize the critical role that farm equipment and repair play in enhancing agricultural operations. By maintaining and investing in reliable grain storage solutions like silos, we can ensure a sustainable future for the agricultural industry.